2024 Federal Budget
Christopher Bowlby - Apr 17, 2024
The 2024 budget continues the trend of tax-and-spend policies with a major reform to capital gains taxes, spending programs on housing, health, infrastructure, Indigenous priorities, and defense, and no clear path to a balanced budget in sight.
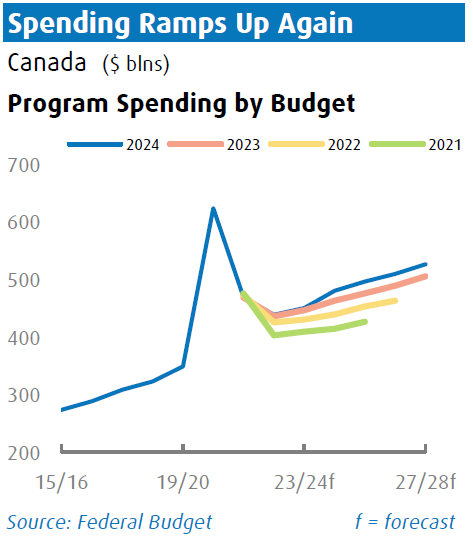
On Tuesday, April 17th, the Liberal Government released their 2024 Federal Budget during a challenging economic period. With the economy struggling, the Bank of Canada is contending with stubborn inflation and a high overnight rate. There's pressure on the Canadian dollar relative to the US dollar and a housing crisis exacerbated by inadequate housing measures and increased immigration. The budget includes a range of spending measures totaling $53 billion over the next five years, with $21.9 billion funded by increases in capital gains taxes and excise duties. The government plans to raise taxes on corporations and wealthy individuals. There is little change to the fiscal path since the Fall Economic Statement, with no clear path to a balanced budget.
The budget prioritizes areas such as housing, health, infrastructure, Indigenous priorities, and defense. A major highlight is the housing measures. To address the country’s housing shortage and fulfill a promise to build 3.87 million new homes by 2031, the Liberals propose using "every possible piece" of federal public land, from armouries to office buildings and post offices. Additionally, the budget introduces a provision allowing first-time home buyers to take out 30-year mortgages for newly built homes.
Overall, the 2024 budget continues the trend of tax-and-spend policies, and the ongoing deficits will complicate the Bank of Canada’s efforts to manage the economy.
Summary of Personal Income Tax Measures
Changes to Capital Gains Inclusion Rate
The capital gains inclusion rate has been a topic of discussion for increasing tax revenues as the government continues to face deficits. Historically, the inclusion rate was 66.66% in 1988 and 1989 and 75% from 1990 to 1999 before dropping to 50% in 2001.
In the 2024 budget, the inclusion rate for capital gains is raised to 66.66% from 50% for two groups: corporations and trusts, and individuals, either directly or indirectly via partnerships or trusts, realizing over $250,000 net in gains. This change will be effective from June 25th.
An individual claiming the employee stock option deduction will now be eligible for a 33% deduction of the taxable benefit, though they remain entitled to a deduction of 50% of the benefit up to a combined limit of $250,000 for both employee stock options and capital gains.
With the new capital gains inclusion rate effective in June, two different rates will apply for 2024, and taxpayers will be subject to the higher rate for the portion of net gains exceeding $250,000 that arise after June 24th.
Lifetime Capital Gains Exemption
The budget also increases the Lifetime Capital Gains Exemption from $1 million to $1.25 million, applicable on the sale of qualified small business and qualified farming or fishing property.
RRSP Home Buyer’s Plan
Earlier in the week, the Federal government announced an increase in the HBP withdrawal limit from $35,000 to $60,000.
Canadian Entrepreneurs’ Incentive
The government proposes a new incentive to encourage entrepreneurship by reducing the tax rates on capital gains from the sale of qualifying shares by an eligible individual. This incentive provides for a capital gains inclusion rate that is half the prevailing rate on a lifetime maximum of up to $2M in eligible capital gains per individual. The lifetime limit will phase in by increments of $200,000 per year, starting January 1, 2025, reaching $2M by January 1, 2034.
Under the two-thirds capital gains inclusion rate proposed in the 2024 Budget, this measure would result in an inclusion rate of 33.3% for dispositions of qualifying shares of a corporation. When combined with the (increased) enhanced LCGE of $1.25M, entrepreneurs can benefit from a combined full or partial exemption of at least $3.25M when selling all or part of a qualifying business.
Alternative Minimum Tax
The 2024 Budget proposes several amendments to the AMT, based on last year’s proposed changes. Among the amendments, individuals will now be able to claim 80% of charitable donations when calculating the AMT, as opposed to the originally proposed 50%.
Employee Ownership Trusts
Further details on Employee Ownership Trusts (EOTs), introduced last year, were provided. An EOT allows a trust to hold shares of a corporation for the benefit of the corporation's employees. It facilitates the purchase of a business by its employees and provides business owners an additional exit strategy. If the conditions of the EOT are satisfied, individuals can claim an exemption up to $10 million in capital gains from the sale. If multiple individuals dispose of shares to an EOT and meet the conditions, they may each claim the exemption, but the total exemption cannot exceed $10M. The individuals must agree on how to allocate the exemption.
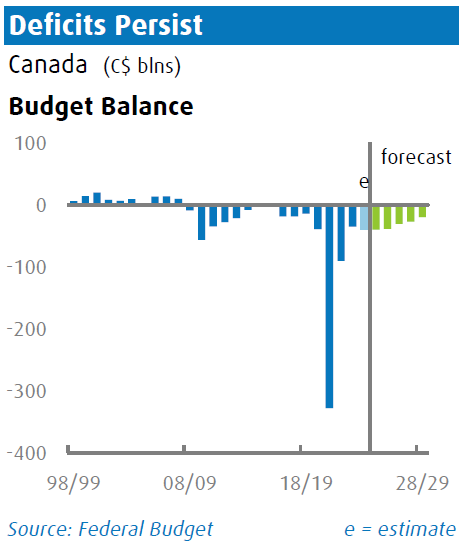
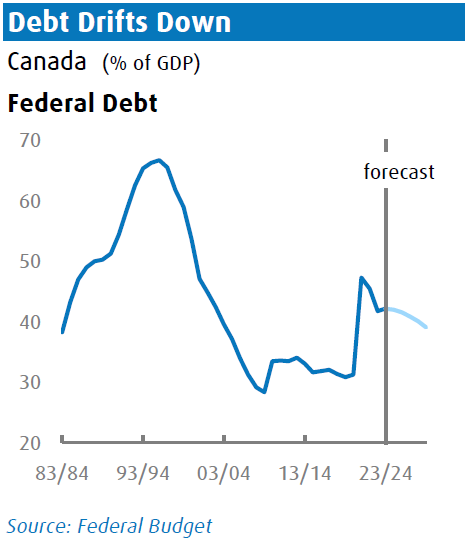
Fiscal Outlook
The budget deficit is estimated at $39 .8 billion for FY24/25, remaining consistent with FY23/24. Tax revenues are expected to rise by a solid 6.7% in FY24/25, counterbalanced by a spending increase of the same percentage. The debt-to-GDP ratio is projected to decrease to 41.9% in the coming fiscal year, from 42.1% in FY23/24, and is expected to gradually decline to just under 40% by FY28/29.