CPP Explained
Debbie Bongard - Nov 15, 2018
This article explains some information on CPP benefits, the pros and cons of taking the pension early or late and some information on the CPP enhancements starting in 2019.

CPP – Explained
The Canadian Pension Plan (CPP) is a government pension that is paid to Canadians who have contributed to the pension plan during their working years. The Canadian Pension Plan is a defined benefit pension plan which provides you a fixed monthly income, indexed with inflation based upon the amount you contributed while you were working.
How It Works
The Canadian Pension Plan is funded with contributions from working Canadians and the CPP Investment Board (CPPIB) then invests the funds in a variety of investments around the world to generate income to be distributed to Canadian pensioners.
CPP contributions are usually taken directly from your paycheck and contributions are equally divided between employee and employer at a rate of 4.95%, for a total of 9.90%. These contributions continue to the CRA’s Yearly Maximum Pensionable Earnings limit (YPME), for 2018 this amount is $55,900. (Note: The first $3,500 of income is exempt for CPP contributions). The maximum contribution for employees and employers for 2018 is $2,593.90 each.
Similar to OAS, your CPP contribution benefit is based on your years of contribution to CPP. If you have contributed to CPP for approximately 40 years and have earned more than the YMPE in each of those years, there is a very high likelihood that you will earn the maximum CPP contribution of $1,134.17 per month or $13,616.52 per year. To find more information on how much you will receive in CPP, contact the CRA for more details about your situation.
Early or Late
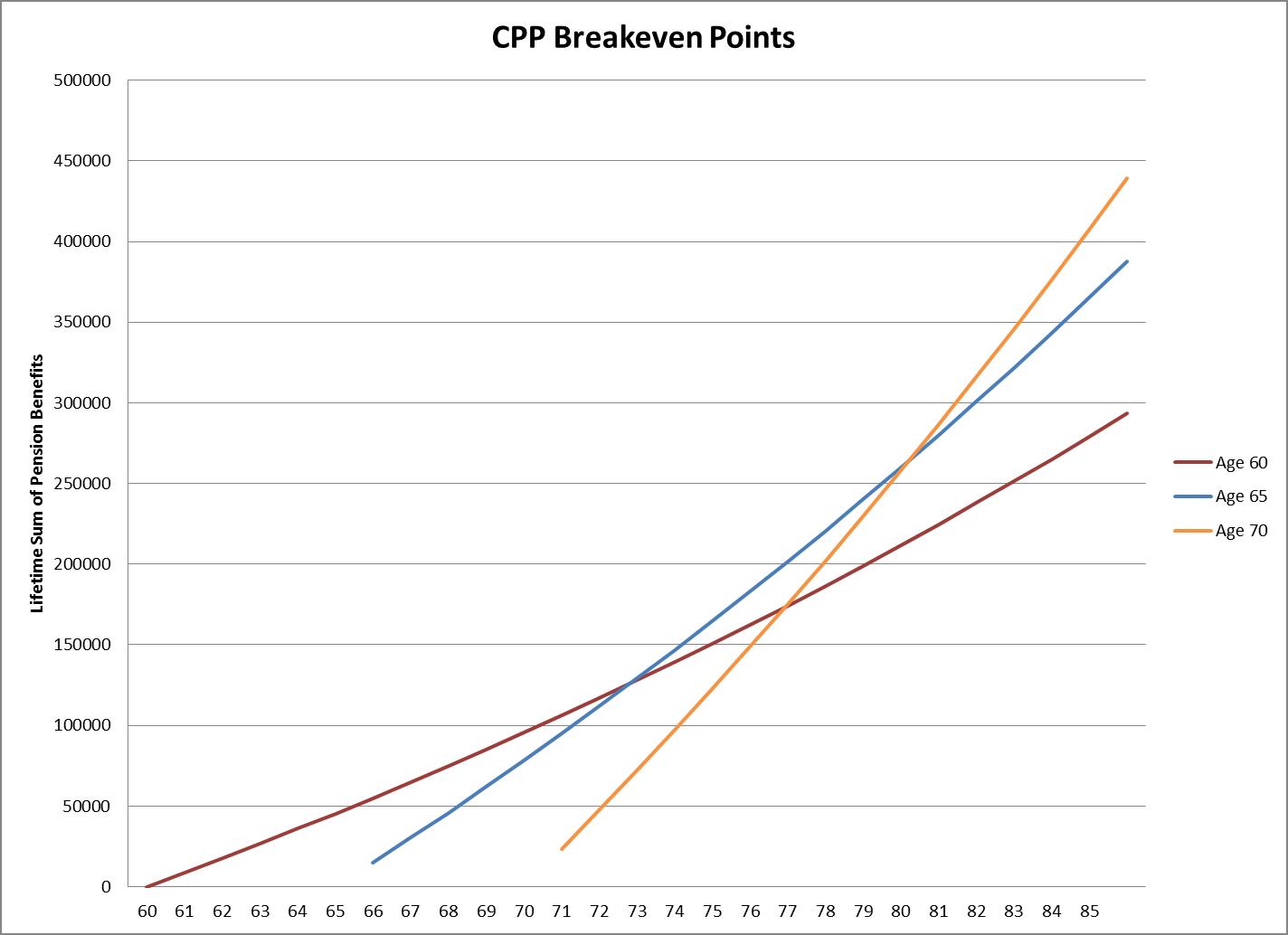
One of the main questions we are asked regarding CPP is whether CPP should be taken early or postponed. The standard retirement age for CPP is age 65, but there is flexibility in taking the pension as soon as 60 and as late as 70.
If CPP is taken early, the pension will be reduced by an amount of 0.6% per month; and if the pension is taken as soon as possible, age 60, the pension benefits will be decreased by 36%. For a pensioner scheduled to receive the maximum CPP benefits in 2018, their pension would decline to $8,709.12 per year or $725.76 per month.
If CPP is taken late, the pension will be increased by an amount of 0.7% per month, and if the pension is taken as late as possible, age 70, the pension benefits will be increased by 42%. For a pensioner scheduled to receive the maximum CPP benefits in 2018, their pension would increase to $19,326.26 per year or $1,610.52 per month.
The decision on when to take CPP is based on many different factors with the main one being your life expectancy and potential health issues. By taking the CPP early, you can guarantee to receive a pension from CPP before any health issues may arise and change your retirement plans.
By deferring your CPP, you are receiving a higher pension benefit, but you are taking more longevity risk. The breakeven point for taking CPP after age 65 versus taking it earlier is pushed out, and if you were not to survive to the break-even point, you would not be maximizing your pensions benefits.
Another primary consideration for when to take CPP is your other sources of income and if you are still working. If you have other sources of retirement income or are still working past age 65, you may want to entertain the idea of postponing your CPP as the extra income would increase your taxes payable, and you would receive a more substantial lifetime benefit waiting until you need the funds.
On the contrary, if you, like many Canadians in 2018, will be reliant upon self-directed RRSPs or Defined Contribution Pension Plans to fund your retirement, you will not have a consistent source of income during retirement besides your retirement savings, and may want to consider taking your CPP at retirement to have another source of retirement income.
CPP Improvements
In 2019, CPP will be implementing improvements to allow the CPP to provide Canadians with larger pensions in retirement. With the enhancements, the CPP will replace more of Canadians incomes in retirement, increasing from 25% to 33% of the YMPE. In simple terms, the current maximum annual retirement pension of $13,610 would be worth approximately $20,750 in 2018 dollars by the time the CPP enhancement process is completed – an extra $7,140 a year.
With the CPP improvements, there will also be an increase in contributions by Canadians from 4.95% to 5.95% by both employees and employers so that you may see a slight decrease in your paycheck over the next few years as a result of the planned contribution increases.

Other CPP Facts
-
For individuals living in Quebec, there is the Quebec Pension Plan that provided similar pensions and benefits to the CPP
-
CPP can be used for income splitting providing an additional benefit of tax minimization during retirement
-
There are provisions in CPP for Canadians who are completely disabled to receive a pension benefit before the age of 60
-
The CPP has a survivor benefit component of 60% of the deceased pension’s to their spouse
-
If you are working between age 65 and 70, you can still contribute to CPP increasing
-
CPP has child rearing provisions if you leave the workforce or work less working houses to compensate you for being the primary caregiver for a child under the age of 7
-
CPP has a drop out provision to protect you for up to eight years for reasons such as t going to school, becoming unemployed or leaving the workforce to provide care to a family member.